How to use Seeq and TDengine to perform time series data analysis
Introduction
Seeq is an advanced analytics software for the manufacturing industry and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Seeq supports the use of machine learning innovations within process manufacturing organizations. These capabilities enable organizations to deploy their own or third-party machine learning algorithms into advanced analytics applications used by frontline process engineers and subject matter experts, thus extending the efforts of a single data scientist to many frontline workers.
TDengine can be added as a data source into Seeq via JDBC client library. Once data source is configured, Seeq can read data from TDengine and offers functionalities such as data visualization, analysis, and forecasting.
Prerequisite
- Install Seeq Server and Seeq Data Lab software
- Install TDengine or register TDengine Cloud service
Install TDengine JDBC client library
- Get Seeq data location configuration
sudo seeq config get Folders/Data
- Download the latest TDengine Java client library from maven.org (current is version is 3.2.5), and copy the JAR file into the_directory_found_in_step_1/plugins/lib/
- Restart Seeq server
sudo seeq restart
Add TDengine into Seeq's data source
- Open Seeq, login as admin, go to Administration, click "Add Data Source"
- For connector, choose SQL connector v2
- Inside "Additional Configuration" input box, copy and paste the following
{
"QueryDefinitions": []
"Type": "GENERIC",
"Hostname": null,
"Port": 0,
"DatabaseName": null,
"Username": null,
"Password": null,
"InitialSql": null,
"TimeZone": null,
"PrintRows": false,
"UseWindowsAuth": false,
"SqlFetchBatchSize": 100000,
"UseSSL": false,
"JdbcProperties": null,
"GenericDatabaseConfig": {
"DatabaseJdbcUrl": "jdbc:TAOS-RS://localhost:6030/?user=root&password=taosdata",
"SqlDriverClassName": "com.taosdata.jdbc.rs.RestfulDriver",
"ResolutionInNanoseconds": 1000,
"ZonedColumnTypes": []
}
}
Note: You need to replace DatabaseJdbcUrl with your setting. Please login TDengine cloud or open taosExplorer for enterprise edition, click programming -> Java to find yours. For the "QueryDefintions", please follow the examples below to write your own.
Use Seeq to analyze time-series data stored inside TDengine
This chapter demonstrates how to use Seeq with TDengine for time series data analysis.
Scenario Overview
The example scenario involves a power system where users collect electricity consumption data from metering devices at a power station on a daily basis. This data is stored in a TDengine cluster. The user now wants to predict how the electricity consumption will develop and purchase additional equipment to support it. The electricity consumption varies with monthly orders, and seasonal variations also affect the power consumption. Since the city is located in the Northern Hemisphere, more electricity is consumed during the summer. We will use simulated data to reflect these assumptions.
Schema
CREATE STABLE meters (ts TIMESTAMP, num INT, temperature FLOAT, goods INT) TAGS (device NCHAR(20));
CREATE TABLE goods (ts1 TIMESTAMP, ts2 TIMESTAMP, goods FLOAT);
Mock data
python mockdata.py
taos -s "insert into power.goods select _wstart, _wstart + 10d, avg(goods) from power.meters interval(10d);"
The source code is hosted at GitHub Repository.
Using Seeq for data analysis
Data Source configuration
Please login with Seeq administrator and create a few data sources as following.
- Power
{
"QueryDefinitions": [
{
"Name": "PowerNum",
"Type": "SIGNAL",
"Sql": "SELECT ts, num FROM meters",
"Enabled": true,
"TestMode": false,
"TestQueriesDuringSync": true,
"InProgressCapsulesEnabled": false,
"Variables": null,
"Properties": [
{
"Name": "Name",
"Value": "Num",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Interpolation Method",
"Value": "linear",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Maximum Interpolation",
"Value": "2day",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
}
],
"CapsuleProperties": null
}
],
"Type": "GENERIC",
"Hostname": null,
"Port": 0,
"DatabaseName": null,
"Username": null,
"Password": null,
"InitialSql": null,
"TimeZone": null,
"PrintRows": false,
"UseWindowsAuth": false,
"SqlFetchBatchSize": 100000,
"UseSSL": false,
"JdbcProperties": null,
"GenericDatabaseConfig": {
"DatabaseJdbcUrl": "jdbc:TAOS-RS://127.0.0.1:6041/power?user=root&password=taosdata",
"SqlDriverClassName": "com.taosdata.jdbc.rs.RestfulDriver",
"ResolutionInNanoseconds": 1000,
"ZonedColumnTypes": []
}
}
- Goods
{
"QueryDefinitions": [
{
"Name": "PowerGoods",
"Type": "CONDITION",
"Sql": "SELECT ts1, ts2, goods FROM power.goods",
"Enabled": true,
"TestMode": false,
"TestQueriesDuringSync": true,
"InProgressCapsulesEnabled": false,
"Variables": null,
"Properties": [
{
"Name": "Name",
"Value": "Goods",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Maximum Duration",
"Value": "10days",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
}
],
"CapsuleProperties": [
{
"Name": "goods",
"Value": "${columnResult}",
"Column": "goods",
"Uom": "string"
}
]
}
],
"Type": "GENERIC",
"Hostname": null,
"Port": 0,
"DatabaseName": null,
"Username": null,
"Password": null,
"InitialSql": null,
"TimeZone": null,
"PrintRows": false,
"UseWindowsAuth": false,
"SqlFetchBatchSize": 100000,
"UseSSL": false,
"JdbcProperties": null,
"GenericDatabaseConfig": {
"DatabaseJdbcUrl": "jdbc:TAOS-RS://127.0.0.1:6041/power?user=root&password=taosdata",
"SqlDriverClassName": "com.taosdata.jdbc.rs.RestfulDriver",
"ResolutionInNanoseconds": 1000,
"ZonedColumnTypes": []
}
}
- Temperature
{
"QueryDefinitions": [
{
"Name": "PowerNum",
"Type": "SIGNAL",
"Sql": "SELECT ts, temperature FROM meters",
"Enabled": true,
"TestMode": false,
"TestQueriesDuringSync": true,
"InProgressCapsulesEnabled": false,
"Variables": null,
"Properties": [
{
"Name": "Name",
"Value": "Temperature",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Interpolation Method",
"Value": "linear",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Maximum Interpolation",
"Value": "2day",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
}
],
"CapsuleProperties": null
}
],
"Type": "GENERIC",
"Hostname": null,
"Port": 0,
"DatabaseName": null,
"Username": null,
"Password": null,
"InitialSql": null,
"TimeZone": null,
"PrintRows": false,
"UseWindowsAuth": false,
"SqlFetchBatchSize": 100000,
"UseSSL": false,
"JdbcProperties": null,
"GenericDatabaseConfig": {
"DatabaseJdbcUrl": "jdbc:TAOS-RS://127.0.0.1:6041/power?user=root&password=taosdata",
"SqlDriverClassName": "com.taosdata.jdbc.rs.RestfulDriver",
"ResolutionInNanoseconds": 1000,
"ZonedColumnTypes": []
}
}
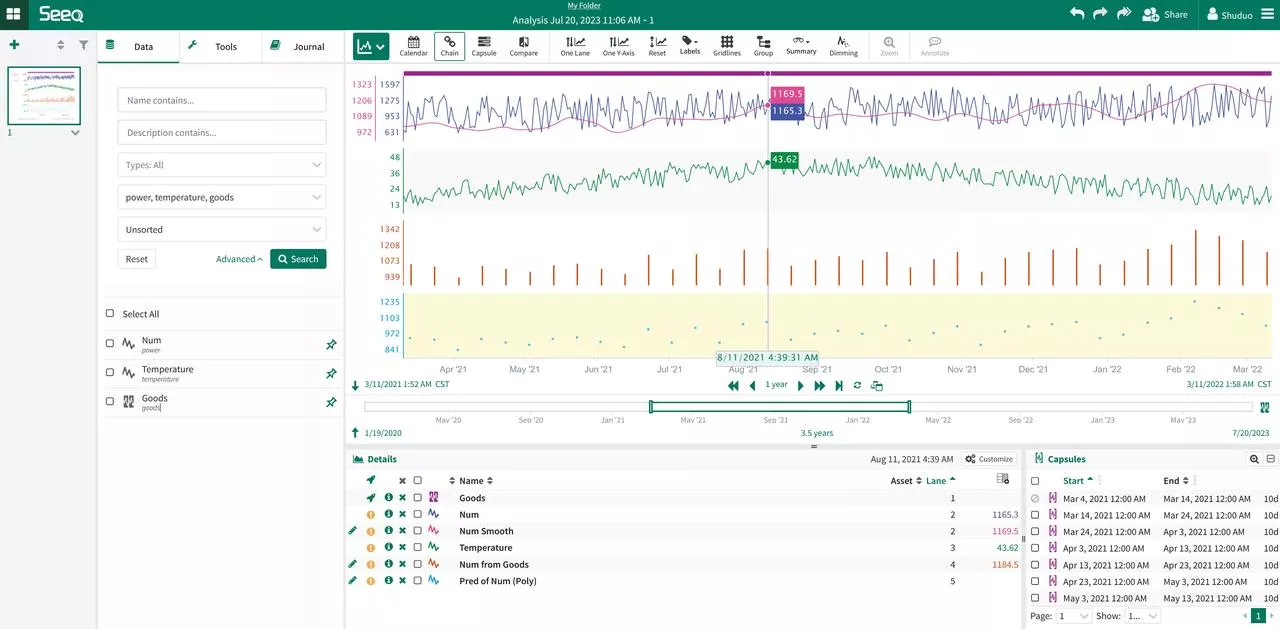
Launch Seeq Workbench
Please login to Seeq server and create a new Seeq Workbench, then select data sources and choose the correct tools to do data visualization and analysis. Please refer to the official documentation for the details.
Use Seeq Data Lab Server for advanced data analysis
Please login to the Seeq service and create a new Seeq Data Lab. Then you can use advanced tools including Python environment and machine learning add-ons for more complex analysis.
from seeq import spy
spy.options.compatibility = 189
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mlforecast
import lightgbm as lgb
from mlforecast.target_transforms import Differences
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
ds = spy.search({'ID': "8C91A9C7-B6C2-4E18-AAAF-XXXXXXXXX"})
print(ds)
sig = ds.loc[ds['Name'].isin(['Num'])]
print(sig)
data = spy.pull(sig, start='2015-01-01', end='2022-12-31', grid=None)
print("data.info()")
data.info()
print(data)
#data.plot()
print("data[Num].info()")
data['Num'].info()
da = data['Num'].index.tolist()
#print(da)
li = data['Num'].tolist()
#print(li)
data2 = pd.DataFrame()
data2['ds'] = da
print('1st data2 ds info()')
data2['ds'].info()
#data2['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(data2['ds']).to_timestamp()
data2['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(data2['ds']).astype('int64')
data2['y'] = li
print('2nd data2 ds info()')
data2['ds'].info()
print(data2)
data2.insert(0, column = "unique_id", value="unique_id")
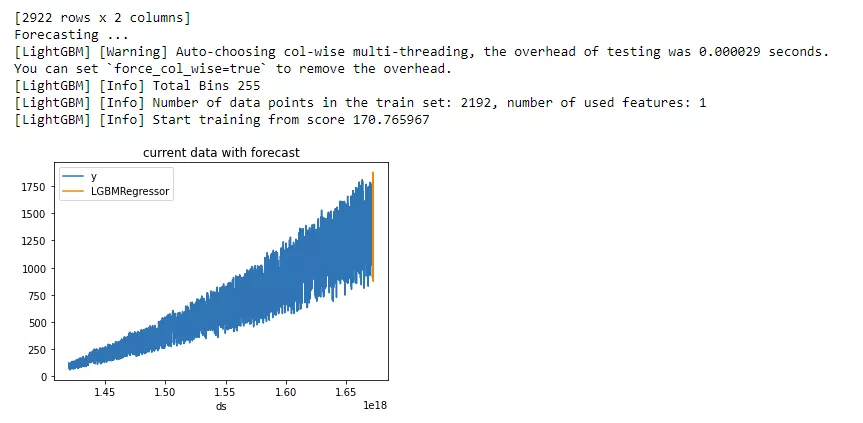
print("Forecasting ...")
forecast = mlforecast.MLForecast(
models = lgb.LGBMRegressor(),
freq = 1,
lags=[365],
target_transforms=[Differences([365])],
)
forecast.fit(data2)
predicts = forecast.predict(365)
pd.concat([data2, predicts]).set_index("ds").plot(title = "current data with forecast")
plt.show()
Example output:
How to configure Seeq data source to access TDengine Cloud
Configuring a Seeq data source connection to TDengine Cloud or a local installation instance does not have any essential differences. After logging in to TDengine Cloud, select "Programming - Java" and copy the JDBC URL string with the token provided. Then, use this JDBC URL string to fill in the DatabaseJdbcUrl value in the Seeq Data Source configuration.
Please note that when using TDengine Cloud, you need to specify the database name in your SQL commands.
The data source of TDengine Cloud example
This data source contains the data from a smart meter in public database smartmeters.
{
"QueryDefinitions": [
{
"Name": "CloudVoltage",
"Type": "SIGNAL",
"Sql": "SELECT ts, voltage FROM smartmeters.d1000",
"Enabled": true,
"TestMode": false,
"TestQueriesDuringSync": true,
"InProgressCapsulesEnabled": false,
"Variables": null,
"Properties": [
{
"Name": "Name",
"Value": "Voltage",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Interpolation Method",
"Value": "linear",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
},
{
"Name": "Maximum Interpolation",
"Value": "2day",
"Sql": null,
"Uom": "string"
}
],
"CapsuleProperties": null
}
],
"Type": "GENERIC",
"Hostname": null,
"Port": 0,
"DatabaseName": null,
"Username": null,
"Password": null,
"InitialSql": null,
"TimeZone": null,
"PrintRows": false,
"UseWindowsAuth": false,
"SqlFetchBatchSize": 100000,
"UseSSL": false,
"JdbcProperties": null,
"GenericDatabaseConfig": {
"DatabaseJdbcUrl": "jdbc:TAOS-RS://gw.us-west-2.aws.cloud.tdengine.com?useSSL=true&token=42b874395452d36f38dd6bf4317757611b213683",
"SqlDriverClassName": "com.taosdata.jdbc.rs.RestfulDriver",
"ResolutionInNanoseconds": 1000,
"ZonedColumnTypes": []
}
}
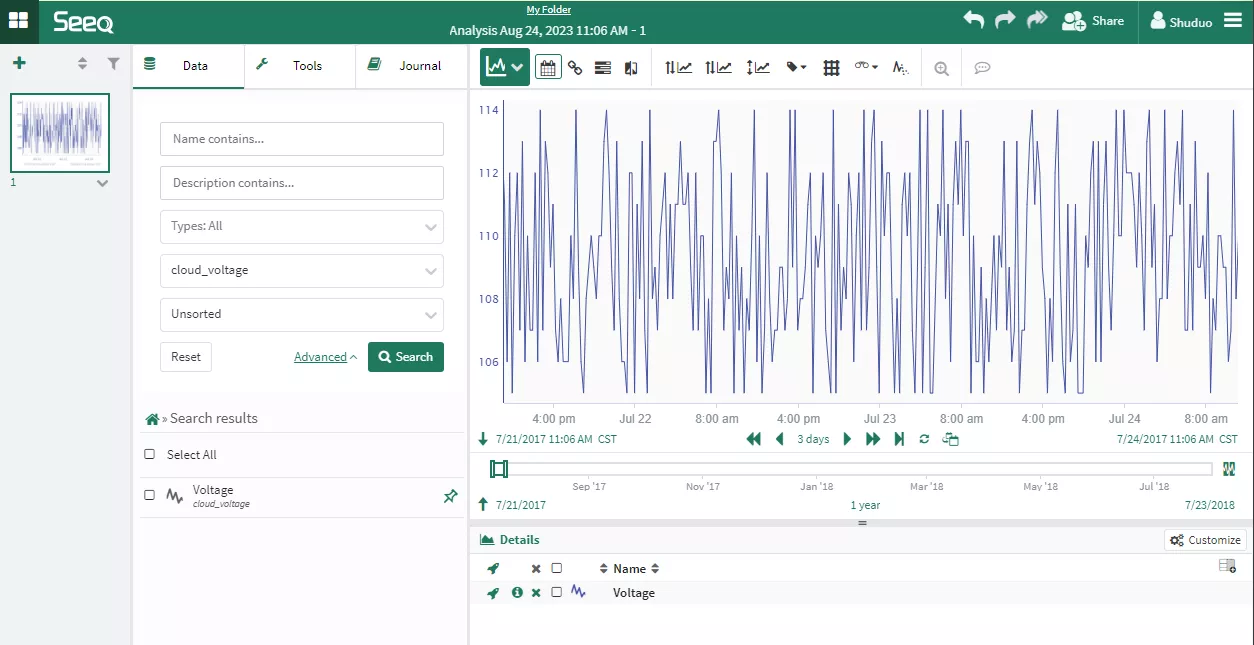
Seeq Workbench with TDengine Cloud data source example
Conclusion
By integrating Seeq and TDengine, you can leverage the efficient storage and querying performance of TDengine while also benefiting from Seeq's powerful data visualization and analysis capabilities provided to users.
This integration allows users to take advantage of TDengine's high-performance time-series data storage and query, ensuring efficient handling of large volumes of data. At the same time, Seeq provides advanced analytics features such as data visualization, anomaly detection, correlation analysis, and predictive modeling, enabling users to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Together, Seeq and TDengine provide a comprehensive solution for time series data analysis in diverse industries such as manufacturing, IIoT, and power systems. The combination of efficient data storage and advanced analytics empowers users to unlock the full potential of their time series data, driving operational improvements, and enabling predictive and prescriptive analytics applications.
