Java connector
Introduction
The taos-jdbcdriver is implemented in two forms: JDBC-JNI and JDBC-RESTful (supported from taos-jdbcdriver-2.0.18). JDBC-JNI is implemented by calling the local methods of libtaos.so (or taos.dll) on the client, while JDBC-RESTful encapsulates the RESTful interface implementation internally.
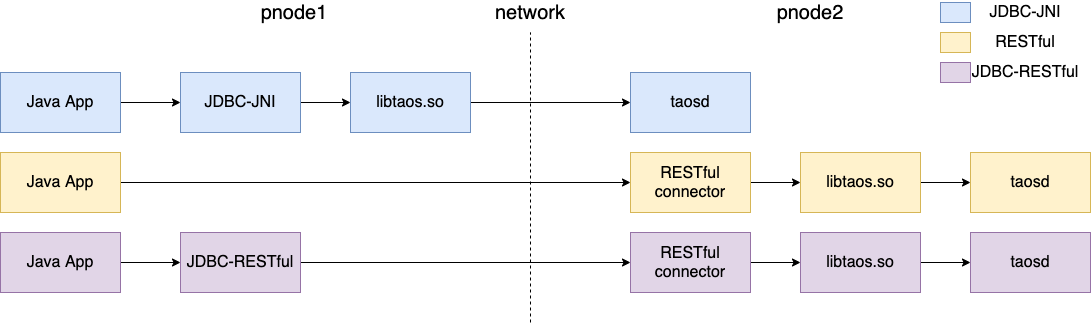
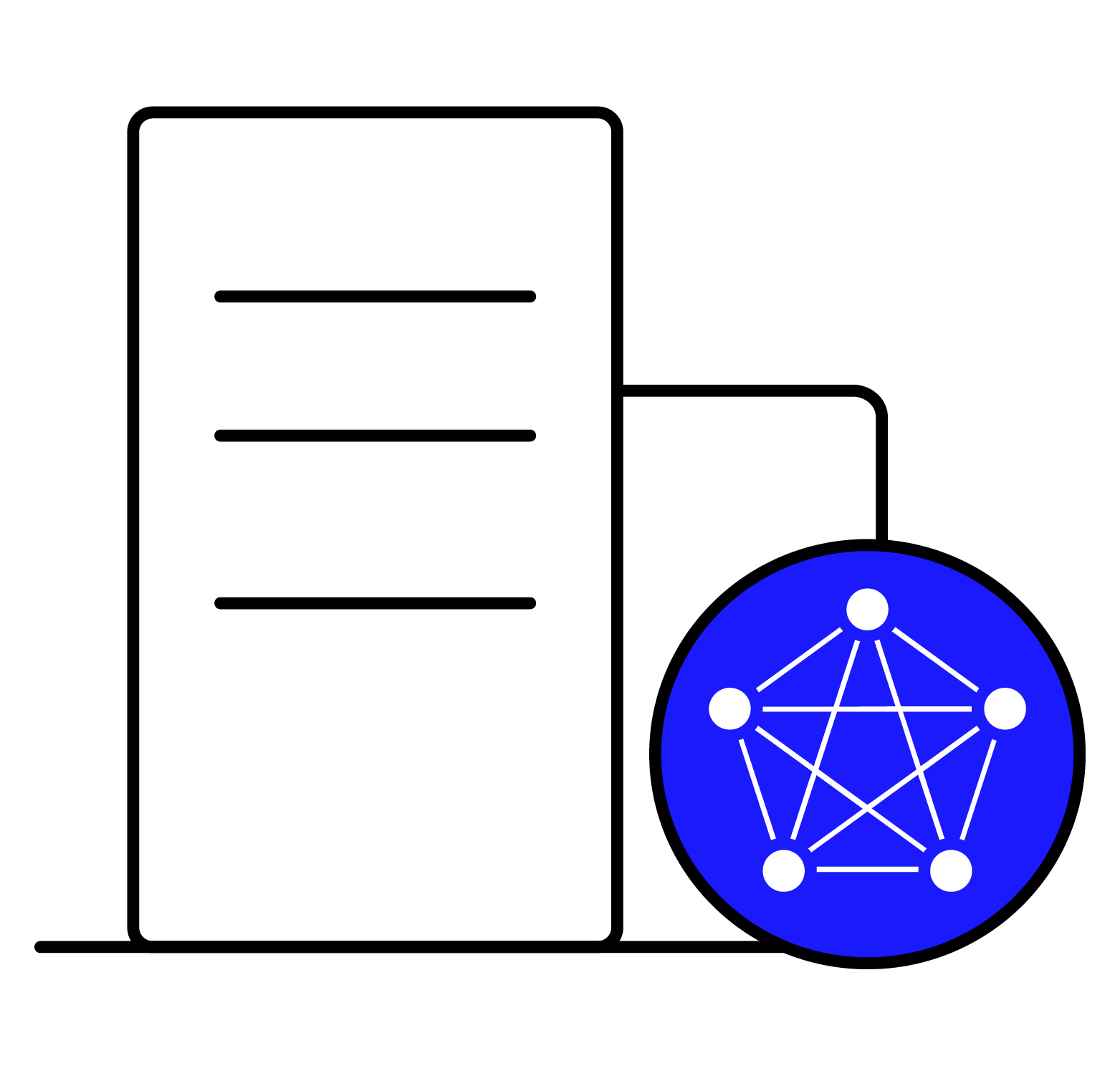
The figure above shows the three ways Java applications can access the TDengine:
- JDBC-JNI: The Java application uses JDBC-JNI's API on physical node1 (pnode1) and directly calls the client API (libtaos.so or taos.dll) to send write or query requests to the taosd instance on physical node2 (pnode2).
- RESTful: The Java application sends the SQL to the RESTful connector on physical node2 (pnode2), which then calls the client API (libtaos.so).
- JDBC-RESTful: The Java application uses the JDBC-restful API to encapsulate SQL into a RESTful request and send it to the RESTful connector of physical node 2.
In terms of implementation, the JDBC driver of TDengine is as consistent as possible with the behavior of the relational database driver. However, due to the differences between TDengine and relational database in the object and technical characteristics of services, there are some differences between taos-jdbcdriver and traditional relational database JDBC driver. The following points should be watched:
- deleting a record is not supported in TDengine.
- transaction is not supported in TDengine.
Difference between JDBC-JNI and JDBC-restful
| Difference | JDBC-JNI | JDBC-RESTful |
|---|---|---|
| Supported OS | Linux, Windows | all platform |
| Whether to install the Client | need | do not need |
| Whether to upgrade the client after the server is upgraded | need | do not need |
| Write performance | JDBC-RESTful is 50% to 90% of JDBC-JNI | |
| Read performance | JDBC-RESTful is no different from JDBC-JNI | |
Note: RESTful interfaces are stateless. Therefore, when using JDBC-restful, you should specify the database name in SQL before all table names and super table names, for example:
INSERT INTO test.t1 USING test.weather (ts, temperature) TAGS('beijing') VALUES(now, 24.6);
JDBC driver version and supported TDengine and JDK versions
| taos-jdbcdriver version | TDengine 2.0.x.x version | TDengine 2.2.x.x version | TDengine 2.4.x.x version | JDK version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0.38 | X | X | 2.4.0.14 or later | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.37 | X | X | 2.4.0.6 or later | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.36 | X | 2.2.2.11 or later | 2.4.0.0 - 2.4.0.5 | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.35 | X | 2.2.2.11 or later | 2.3.0.0 - 2.4.0.5 | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.33 - 2.0.34 | 2.0.3.0 or later | 2.2.0.0 or later | 2.4.0.0 - 2.4.0.5 | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.31 - 2.0.32 | 2.1.3.0 - 2.1.7.7 | X | X | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.22 - 2.0.30 | 2.0.18.0 - 2.1.2.1 | X | X | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.12 - 2.0.21 | 2.0.8.0 - 2.0.17.4 | X | X | 1.8.x |
| 2.0.4 - 2.0.11 | 2.0.0.0 - 2.0.7.3 | X | X | 1.8.x |
DataType in TDengine and Java connector
The TDengine supports the following data types and Java data types:
| TDengine DataType | JDBCType (driver version < 2.0.24) | JDBCType (driver version >= 2.0.24) |
|---|---|---|
| TIMESTAMP | java.lang.Long | java.sql.Timestamp |
| INT | java.lang.Integer | java.lang.Integer |
| BIGINT | java.lang.Long | java.lang.Long |
| FLOAT | java.lang.Float | java.lang.Float |
| DOUBLE | java.lang.Double | java.lang.Double |
| SMALLINT | java.lang.Short | java.lang.Short |
| TINYINT | java.lang.Byte | java.lang.Byte |
| BOOL | java.lang.Boolean | java.lang.Boolean |
| BINARY | java.lang.String | byte array |
| NCHAR | java.lang.String | java.lang.String |
| JSON | - | java.lang.String |
| Note: JSON type can only be used in tag. |
Install Java connector
Runtime Requirements
To run TDengine's Java connector, the following requirements shall be met:
-
A Linux or Windows System
-
Java Runtime Environment 1.8 or later
-
TDengine client (required for JDBC-JNI, not required for JDBC-restful)
Note:
- After the TDengine client is successfully installed on Linux, the libtaos.so file is automatically copied to /usr/lib/libtaos.so, which is included in the Linux automatic scan path and does not need to be specified separately.
- After the TDengine client is installed on Windows, the taos.dll file that the driver package depends on is automatically copied to the default search path C:/Windows/System32. You do not need to specify it separately.
Obtain JDBC driver by maven
To Java developers, TDengine provides taos-jdbcdriver according to the JDBC(3.0) API. Users can find and download it through Sonatype Repository. Add the following dependencies in pom.xml for your maven projects.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.taosdata.jdbc</groupId>
<artifactId>taos-jdbcdriver</artifactId>
<version>2.0.34</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Obtain JDBC driver by compiling source code
You can download the TDengine source code and compile the latest version of the JDBC Connector.
git clone https://github.com/taosdata/TDengine.git
cd TDengine/src/connector/jdbc
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
a taos-jdbcdriver-2.0.xx-dist.jar will be released in the target directory.
Usage of java connector
Establishing a Connection
Establishing a connection with URL
Establish the connection by specifying the URL, as shown below:
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS-RS://taosdemo.com:6041/test?user=root&password=taosdata";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl);
In the example above, the JDBC-RESTful driver is used to establish a connection to the hostname of 'taosdemo.com', port of 6041, and database name of 'test'. This URL specifies the user name as 'root' and the password as 'taosdata'.
The JDBC-RESTful does not depend on the local function library. Compared with JDBC-JNI, only the following is required:
- DriverClass designated as "com.taosdata.jdbc.rs.RestfulDriver"
- JdbcUrl starts with "JDBC:TAOS-RS://"
- Use port 6041 as the connection port
JDBC 2.0.38 and later version with TDengine 2.4.0.12 (and later version) start to support a new bulk-pulling feature. It provides higher data transmission performance and larger volume data queries capability via WebSocket communication.
Create bulk-pulling connection:
String url = "jdbc:TAOS-RS://taosdemo.com:6041/?user=root&password=taosdata";Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_BATCH_LOAD, "true");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
For better write and query performance, Java applications can use the JDBC-JNI driver, as shown below:
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS://taosdemo.com:6030/test?user=root&password=taosdata";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl);
In the example above, The JDBC-JNI driver is used to establish a connection to the hostname of 'taosdemo.com', port 6030 (TDengine's default port), and database name of 'test'. This URL specifies the user name as 'root' and the password as 'taosdata'.
The format of JDBC URL is:
jdbc:[TAOS|TAOS-RS]://[host_name]:[port]/[database_name]?[user={user}|&password={password}|&charset={charset}|&cfgdir={config_dir}|&locale={locale}|&timezone={timezone}]
The configuration parameters in the URL are as follows:
- user: user name for logging in to the TDengine. The default value is 'root'.
- password: the user login password. The default value is 'taosdata'.
- cfgdir: directory of the client configuration file. It is valid only for JDBC-JNI. The default value is
/etc/taoson Linux andC:/TDengine/cfgon Windows. - charset: character set used by the client. The default value is the system character set.
- locale: client locale. The default value is the current system locale.
- timezone: timezone used by the client. The default value is the current timezone of the system.
- batchfetch: True if batch ResultSet fetching is enabled; false if row-by-row ResultSet fetching is enabled. Default value is false.
- timestampFormat: only valid for JDBC-RESTful. 'TIMESTAMP' if you want to get a long value in a ResultSet; 'UTC' if you want to get a string in UTC date-time format in a ResultSet; 'STRING' if you want to get a local date-time format string in ResultSet. Default value is 'STRING'.
- batchErrorIgnore: true if you want to continue executing the rest of the SQL when error happens during execute the executeBatch method in Statement; false, false if the remaining SQL statements are not executed. Default value is false.
Establishing a connection with URL and Properties
In addition to establish the connection with the specified URL, you can also use Properties to specify the parameters to set up the connection, as shown below:
public Connection getConn() throws Exception{
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS://taosdemo.com:6030/test?user=root&password=taosdata";
// String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS-RS://taosdemo.com:6041/test?user=root&password=taosdata";
Properties connProps = new Properties();
connProps.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_CHARSET, "UTF-8");
connProps.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_LOCALE, "en_US.UTF-8");
connProps.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_TIME_ZONE, "UTC-8");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, connProps);
return conn;
}
In the example above, JDBC-JNI is used to establish a connection to hostname of 'taosdemo.com', port at 6030, and database name of 'test'. The annotation is the method when using JDBC-RESTful. The connection specifies the user name as 'root' and the password as 'taosdata' in the URL, and the character set to use, locale, time zone, and so on in connProps.
The configuration parameters in properties are as follows:
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_USER: user name for logging in to the TDengine. The default value is 'root'.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_PASSWORD: the user login password. The default value is 'taosdata'.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_CONFIG_DIR: directory of the client configuration file. It is valid only for JDBC-JNI. The default value is
/etc/taoson Linux andC:/TDengine/cfg on Windows. - TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_CHARSET: character set used by the client. The default value is the system character set.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_LOCALE: client locale. The default value is the current system locale.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_TIME_ZONE: timezone used by the client. The default value is the current timezone of the system.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_BATCH_LOAD: only valid for JDBC-JNI. True if batch ResultSet fetching is enabled; false if row-by-row ResultSet fetching is enabled. Default value is false.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_TIMESTAMP_FORMAT: only valid for JDBC-RESTful. 'TIMESTAMP' if you want to get a long value in a ResultSet; 'UTC' if you want to get a string in UTC date-time format in a ResultSet; 'STRING' if you want to get a local date-time format string in ResultSet. Default value is 'STRING'.
- TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_BATCH_ERROR_IGNORE: true if you want to continue executing the rest of the SQL when error happens during execute the executeBatch method in Statement; false, false if the remaining SQL statements are not executed. Default value is false.
Establishing a connection with configuration file
When JDBC-JNI is used to connect to the TDengine cluster, you can specify firstEp and secondEp parameters of the cluster in the client configuration file. As follows:
- The hostname and port are not specified in Java applications
public Connection getConn() throws Exception{
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS://:/test?user=root&password=taosdata";
Properties connProps = new Properties();
connProps.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_CHARSET, "UTF-8");
connProps.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_LOCALE, "en_US.UTF-8");
connProps.setProperty(TSDBDriver.PROPERTY_KEY_TIME_ZONE, "UTC-8");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, connProps);
return conn;
}
- Specify firstEp and secondEp in the configuration file
# first fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for TDengine system
firstEp cluster_node1:6030
# second fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for TDengine system, for cluster only
secondEp cluster_node2:6030
In the above example, JDBC driver uses the client configuration file to establish a connection to the hostname of 'cluster_node1', port 6030, and database name of 'test'. When the firstEp node in the cluster fails, JDBC will try to connect to the cluster using secondEp. In the TDengine, as long as one node in firstEp and secondEp is valid, the connection to the cluster can be established.
Note: In this case, the configuration file belongs to TDengine client which is running inside a Java application. default file path of Linux OS is '/etc/taos/taos.cfg', and default file path of Windows OS is 'C://TDengine/cfg/taos.cfg'.
Priority of the parameters
If the parameters in the URL, Properties, and client configuration file are repeated set, the priorities of the parameters in descending order are as follows:
- URL parameters
- Properties
- Client configuration file in taos.cfg
For example, if you specify password as 'taosdata' in the URL and password as 'taosdemo' in the Properties, JDBC will establish a connection using the password in the URL.
For details, see TDengine Operation and Maintenance
Create database and table
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
// create database
stmt.executeUpdate("create database if not exists db");
// use database
stmt.executeUpdate("use db");
// create table
stmt.executeUpdate("create table if not exists tb (ts timestamp, temperature int, humidity float)");
Insert
// insert data
int affectedRows = stmt.executeUpdate("insert into tb values(now, 23, 10.3) (now + 1s, 20, 9.3)");
System.out.println("insert " + affectedRows + " rows.");
Note: 'now' is an internal system function. The default value is the current time of the computer where the client resides. 'now + 1s' indicates that the current time on the client is added by one second. The following time units are a(millisecond), s (second), m(minute), h(hour), d(day), w(week), n(month), and y(year).
Query
// query data
ResultSet resultSet = stmt.executeQuery("select * from tb");
Timestamp ts = null;
int temperature = 0;
float humidity = 0;
while(resultSet.next()){
ts = resultSet.getTimestamp(1);
temperature = resultSet.getInt(2);
humidity = resultSet.getFloat("humidity");
System.out.printf("%s, %d, %s\n", ts, temperature, humidity);
}
Note: The query is consistent with the operation of the relational database, and the index in ResultSet starts from 1.
Handle exceptions
try (Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
// executeQuery
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// print result
printResult(resultSet);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("ERROR Message: " + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("ERROR Code: " + e.getErrorCode());
e.printStackTrace();
}
The Java connector may report three types of error codes: JDBC Driver (error codes ranging from 0x2301 to 0x2350), JNI method (error codes ranging from 0x2351 to 0x2400), and TDengine Error. For details about the error code, see:
https://github.com/taosdata/TDengine/blob/develop/src/connector/jdbc/src/main/java/com/taosdata/jdbc/TSDBErrorNumbers.javahttps://github.com/taosdata/TDengine/blob/develop/src/inc/taoserror.h
Write data through parameter binding
Starting with version 2.1.2.0, TDengine's JDBC-JNI implementation significantly improves support for data write (INSERT) scenarios with Parameter-Binding. When writing data in this way, you can avoid the resource consumption of SQL parsing, which can significantly improve write performance in many cases.
Note:
- JDBC-RESTful implementations do not provide Parameter-Binding
- The following sample code is based on taos-jdbcdriver-2.0.36
- use setString to bind BINARY data, and use setNString to bind NCHAR data
- Both setString and setNString require the user to declare the column width of the corresponding column in the table definition in the size parameter
Sample Code:
public class ParameterBindingDemo {
private static final String host = "127.0.0.1";
private static final Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
private static final int BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE = 20;
private static final String[] schemaList = {
"create table stable1(ts timestamp, f1 tinyint, f2 smallint, f3 int, f4 bigint) tags(t1 tinyint, t2 smallint, t3 int, t4 bigint)",
"create table stable2(ts timestamp, f1 float, f2 double) tags(t1 float, t2 double)",
"create table stable3(ts timestamp, f1 bool) tags(t1 bool)",
"create table stable4(ts timestamp, f1 binary(" + BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE + ")) tags(t1 binary(" + BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE + "))",
"create table stable5(ts timestamp, f1 nchar(" + BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE + ")) tags(t1 nchar(" + BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE + "))"
};
private static final int numOfSubTable = 10, numOfRow = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS://" + host + ":6030/";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, "root", "taosdata");
init(conn);
bindInteger(conn);
bindFloat(conn);
bindBoolean(conn);
bindBytes(conn);
bindString(conn);
conn.close();
}
private static void init(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
try (Statement stmt = conn.createStatement()) {
stmt.execute("drop database if exists test_parabind");
stmt.execute("create database if not exists test_parabind");
stmt.execute("use test_parabind");
for (int i = 0; i < schemaList.length; i++) {
stmt.execute(schemaList[i]);
}
}
}
private static void bindInteger(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into ? using stable1 tags(?,?,?,?) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
try (TSDBPreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql).unwrap(TSDBPreparedStatement.class)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= numOfSubTable; i++) {
// set table name
pstmt.setTableName("t1_" + i);
// set tags
pstmt.setTagByte(0, Byte.parseByte(Integer.toString(random.nextInt(Byte.MAX_VALUE))));
pstmt.setTagShort(1, Short.parseShort(Integer.toString(random.nextInt(Short.MAX_VALUE))));
pstmt.setTagInt(2, random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
pstmt.setTagLong(3, random.nextLong());
// set columns
ArrayList<Long> tsList = new ArrayList<>();
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
tsList.add(current + j);
pstmt.setTimestamp(0, tsList);
ArrayList<Byte> f1List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f1List.add(Byte.parseByte(Integer.toString(random.nextInt(Byte.MAX_VALUE))));
pstmt.setByte(1, f1List);
ArrayList<Short> f2List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f2List.add(Short.parseShort(Integer.toString(random.nextInt(Short.MAX_VALUE))));
pstmt.setShort(2, f2List);
ArrayList<Integer> f3List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f3List.add(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
pstmt.setInt(3, f3List);
ArrayList<Long> f4List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f4List.add(random.nextLong());
pstmt.setLong(4, f4List);
// add column
pstmt.columnDataAddBatch();
}
// execute column
pstmt.columnDataExecuteBatch();
}
}
private static void bindFloat(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into ? using stable2 tags(?,?) values(?,?,?)";
TSDBPreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql).unwrap(TSDBPreparedStatement.class);
for (int i = 1; i <= numOfSubTable; i++) {
// set table name
pstmt.setTableName("t2_" + i);
// set tags
pstmt.setTagFloat(0, random.nextFloat());
pstmt.setTagDouble(1, random.nextDouble());
// set columns
ArrayList<Long> tsList = new ArrayList<>();
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
tsList.add(current + j);
pstmt.setTimestamp(0, tsList);
ArrayList<Float> f1List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f1List.add(random.nextFloat());
pstmt.setFloat(1, f1List);
ArrayList<Double> f2List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f2List.add(random.nextDouble());
pstmt.setDouble(2, f2List);
// add column
pstmt.columnDataAddBatch();
}
// execute
pstmt.columnDataExecuteBatch();
// close if no try-with-catch statement is used
pstmt.close();
}
private static void bindBoolean(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into ? using stable3 tags(?) values(?,?)";
try (TSDBPreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql).unwrap(TSDBPreparedStatement.class)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= numOfSubTable; i++) {
// set table name
pstmt.setTableName("t3_" + i);
// set tags
pstmt.setTagBoolean(0, random.nextBoolean());
// set columns
ArrayList<Long> tsList = new ArrayList<>();
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
tsList.add(current + j);
pstmt.setTimestamp(0, tsList);
ArrayList<Boolean> f1List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
f1List.add(random.nextBoolean());
pstmt.setBoolean(1, f1List);
// add column
pstmt.columnDataAddBatch();
}
// execute
pstmt.columnDataExecuteBatch();
}
}
private static void bindBytes(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into ? using stable4 tags(?) values(?,?)";
try (TSDBPreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql).unwrap(TSDBPreparedStatement.class)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= numOfSubTable; i++) {
// set table name
pstmt.setTableName("t4_" + i);
// set tags
pstmt.setTagString(0, new String("abc"));
// set columns
ArrayList<Long> tsList = new ArrayList<>();
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
tsList.add(current + j);
pstmt.setTimestamp(0, tsList);
ArrayList<String> f1List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++) {
f1List.add(new String("abc"));
}
pstmt.setString(1, f1List, BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE);
// add column
pstmt.columnDataAddBatch();
}
// execute
pstmt.columnDataExecuteBatch();
}
}
private static void bindString(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into ? using stable5 tags(?) values(?,?)";
try (TSDBPreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql).unwrap(TSDBPreparedStatement.class)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= numOfSubTable; i++) {
// set table name
pstmt.setTableName("t5_" + i);
// set tags
pstmt.setTagNString(0, "北京-abc");
// set columns
ArrayList<Long> tsList = new ArrayList<>();
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++)
tsList.add(current + j);
pstmt.setTimestamp(0, tsList);
ArrayList<String> f1List = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numOfRow; j++) {
f1List.add("北京-abc");
}
pstmt.setNString(1, f1List, BINARY_COLUMN_SIZE);
// add column
pstmt.columnDataAddBatch();
}
// execute
pstmt.columnDataExecuteBatch();
}
}
}
The methods used to set tags are:
public void setTagNull(int index, int type)
public void setTagBoolean(int index, boolean value)
public void setTagInt(int index, int value)
public void setTagByte(int index, byte value)
public void setTagShort(int index, short value)
public void setTagLong(int index, long value)
public void setTagTimestamp(int index, long value)
public void setTagFloat(int index, float value)
public void setTagDouble(int index, double value)
public void setTagString(int index, String value)
public void setTagNString(int index, String value)
The methods used to set columns are:
public void setInt(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Integer> list) throws SQLException
public void setFloat(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Float> list) throws SQLException
public void setTimestamp(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Long> list) throws SQLException
public void setLong(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Long> list) throws SQLException
public void setDouble(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Double> list) throws SQLException
public void setBoolean(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Boolean> list) throws SQLException
public void setByte(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Byte> list) throws SQLException
public void setShort(int columnIndex, ArrayList<Short> list) throws SQLException
public void setString(int columnIndex, ArrayList<String> list, int size) throws SQLException
public void setNString(int columnIndex, ArrayList<String> list, int size) throws SQLException
Data Writing via Schemaless
Starting with version 2.2.0.0, TDengine supports schemaless function. schemaless writing protocol is compatible with InfluxDB's Line Protocol, OpenTSDB's telnet and JSON format protocols, Please see Data Writing
Note:
- JDBC-RESTful implementations do not provide Schemaless-Writing
- The following sample code is based on taos-jdbcdriver-2.0.36
Sample Code:
public class SchemalessInsertTest {
private static final String host = "127.0.0.1";
private static final String lineDemo = "st,t1=3i64,t2=4f64,t3=\"t3\" c1=3i64,c3=L\"passit\",c2=false,c4=4f64 1626006833639000000";
private static final String telnetDemo = "stb0_0 1626006833 4 host=host0 interface=eth0";
private static final String jsonDemo = "{\"metric\": \"meter_current\",\"timestamp\": 1346846400,\"value\": 10.3, \"tags\": {\"groupid\": 2, \"location\": \"Beijing\", \"id\": \"d1001\"}}";
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
final String url = "jdbc:TAOS://" + host + ":6030/?user=root&password=taosdata";
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url)) {
init(connection);
SchemalessWriter writer = new SchemalessWriter(connection);
writer.write(lineDemo, SchemalessProtocolType.LINE, SchemalessTimestampType.NANO_SECONDS);
writer.write(telnetDemo, SchemalessProtocolType.TELNET, SchemalessTimestampType.MILLI_SECONDS);
writer.write(jsonDemo, SchemalessProtocolType.JSON, SchemalessTimestampType.NOT_CONFIGURED);
}
}
private static void init(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
try (Statement stmt = connection.createStatement()) {
stmt.executeUpdate("drop database if exists test_schemaless");
stmt.executeUpdate("create database if not exists test_schemaless");
stmt.executeUpdate("use test_schemaless");
}
}
}
Set client configuration in JDBC
Starting with TDengine-2.3.5.0, JDBC Driver supports setting TDengine client parameters on the first connection of a Java application. The Driver supports jdbcUrl and Properties to set client parameters in JDBC-JNI mode.
Note:
- JDBC-RESTful does not support setting client parameters.
- The client parameters set in the java application are process-level. To update the client parameters, the application needs to be restarted. This is because these client parameters are global that take effect the first time the application is set up.
- The following sample code is based on taos-jdbcdriver-2.0.36.
Sample Code:
public class ClientParameterSetting {
private static final String host = "127.0.0.1";
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
setParameterInJdbcUrl();
setParameterInProperties();
}
private static void setParameterInJdbcUrl() throws SQLException {
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS://" + host + ":6030/?debugFlag=135&asyncLog=0";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, "root", "taosdata");
printDatabase(connection);
connection.close();
}
private static void setParameterInProperties() throws SQLException {
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:TAOS://" + host + ":6030/";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "taosdata");
properties.setProperty("debugFlag", "135");
properties.setProperty("asyncLog", "0");
properties.setProperty("maxSQLLength", "1048576");
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, properties)) {
printDatabase(conn);
}
}
private static void printDatabase(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
try (Statement stmt = connection.createStatement()) {
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("show databases");
ResultSetMetaData meta = rs.getMetaData();
while (rs.next()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= meta.getColumnCount(); i++) {
System.out.print(meta.getColumnLabel(i) + ": " + rs.getString(i) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
Data Subscription
Subscribe
TSDBSubscribe sub = ((TSDBConnection)conn).subscribe("topic", "select * from meters", false);
parameters:
- topic: the unique topic name of the subscription.
- sql: a select statement.
- restart: true if restart the subscription already exists; false if continue the previous subscription.
In the example above, a subscription named 'topic' is created which use the SQL statement 'select * from meters'. If the subscription already exists, it will continue with the previous query progress, rather than consuming all the data from scratch.
Consume
int total = 0;
while(true) {
TSDBResultSet rs = sub.consume();
int count = 0;
while(rs.next()) {
count++;
}
total += count;
System.out.printf("%d rows consumed, total %d\n", count, total);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
The consume method returns a result set containing all the new data so far since the last consume. Make sure to call consume as often as you need (like Thread.sleep(1000) in the example), otherwise you will put unnecessary stress on the server.
Close
sub.close(true);
// release resources
resultSet.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
The close method closes a subscription. If the parameter is true, the subscription progress information is reserved, and a subscription with the same name can be created later to continue consuming data. If false, the subscription progress is not retained.
Note: the connection must be closed; otherwise, a connection leak may occur.
Connection Pool
HikariCP example
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
// jdbc properties
config.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:TAOS://127.0.0.1:6030/log");
config.setUsername("root");
config.setPassword("taosdata");
// connection pool configurations
config.setMinimumIdle(10); //minimum number of idle connection
config.setMaximumPoolSize(10); //maximum number of connection in the pool
config.setConnectionTimeout(30000); //maximum wait milliseconds for get connection from pool
config.setMaxLifetime(0); // maximum lifetime for each connection
config.setIdleTimeout(0); // max idle time for recycle idle connection
config.setConnectionTestQuery("select server_status()"); //validation query
HikariDataSource ds = new HikariDataSource(config); //create datasource
Connection connection = ds.getConnection(); // get connection
Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); // get statement
//query or insert
// ...
connection.close(); // put back to connection pool
}
Druid example
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
// jdbc properties
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.taosdata.jdbc.TSDBDriver");
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("taosdata");
// pool configurations
dataSource.setInitialSize(10);
dataSource.setMinIdle(10);
dataSource.setMaxActive(10);
dataSource.setMaxWait(30000);
dataSource.setValidationQuery("select server_status()");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); // get connection
Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); // get statement
//query or insert
// ...
connection.close(); // put back to connection pool
}
Note:
As of TDengine V1.6.4.1, the function select server_status() is supported specifically for heartbeat detection, so it is recommended to use select server_status() for Validation queries when using connection pools.
Select server_status() returns 1 on success, as shown below.
taos> select server_status();
server_status()|
================
1 |
Query OK, 1 row(s) in set (0.000141s)
Integrated with framework
- Please refer to SpringJdbcTemplate if using taos-jdbcdriver in Spring JdbcTemplate.
- Please refer to springbootdemo if using taos-jdbcdriver in Spring JdbcTemplate.
Example Codes
you see sample code here: JDBC example
FAQ
-
Why does not addBatch and executeBatch provide a performance benefit for executing "batch writes/updates"? Cause:In TDengine's JDBC implementation, SQL statements submitted through the addBatch method are executed in the order in which they are added. This method does not reduce the number of interactions with the server and does not improve performance. Answer:1. Concatenate multiple values in an INSERT statement; 2. Use multi-threaded concurrent insertion; 3. Use the parameter-binding to write
-
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: no taos in java.library.path Cause:The application program cannot find Library function taos Answer:Copy
C:\TDengine\driver\taos.dlltoC:\Windows\System32\on Windows and make a soft link throughln -s /usr/local/taos/driver/libtaos.so.x.x.x.x /usr/lib/libtaos.soon Linux. -
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: taos.dll Can't load AMD 64 bit on a IA 32-bit platform Cause:Currently TDengine only support 64bit JDK Answer:re-install 64bit JDK.
-
For other questions, please refer to Issues