Data Preprocessing
Analysis Workflow
Data must be preprocessed before it can be analyzed by TDgpt. This process is described in the following figure:
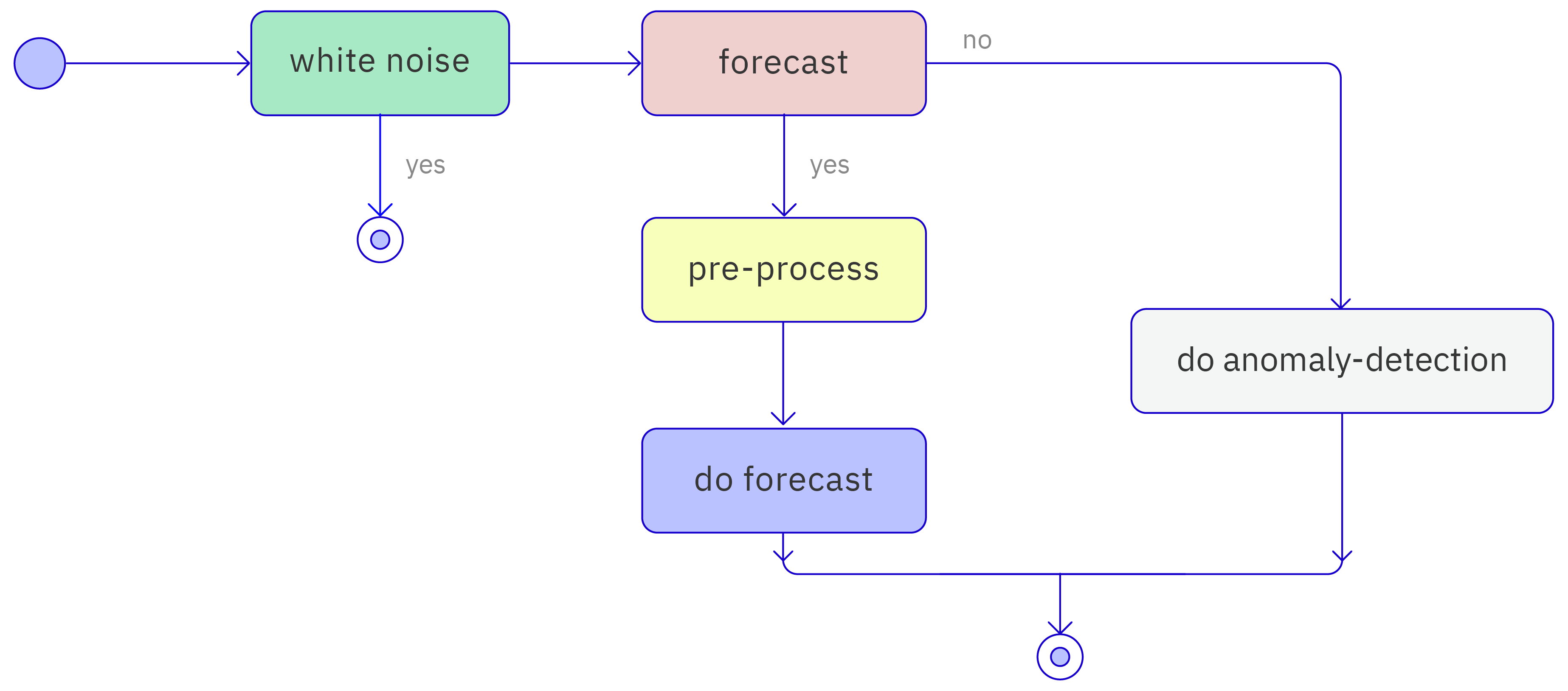
TDgpt first performs a white noise data check on the dataset that you input. Data that passes this check and is intended for use in forecasting is then resampled and its timestamps are aligned. Note that resampling and alignment are not performed for datasets used in anomaly detection.
After the data has been preprocessed, forecasting or anomaly detection is performed. Preprocessing is not part of the business logic for forecasting and anomaly detection.
White Noise Data Check
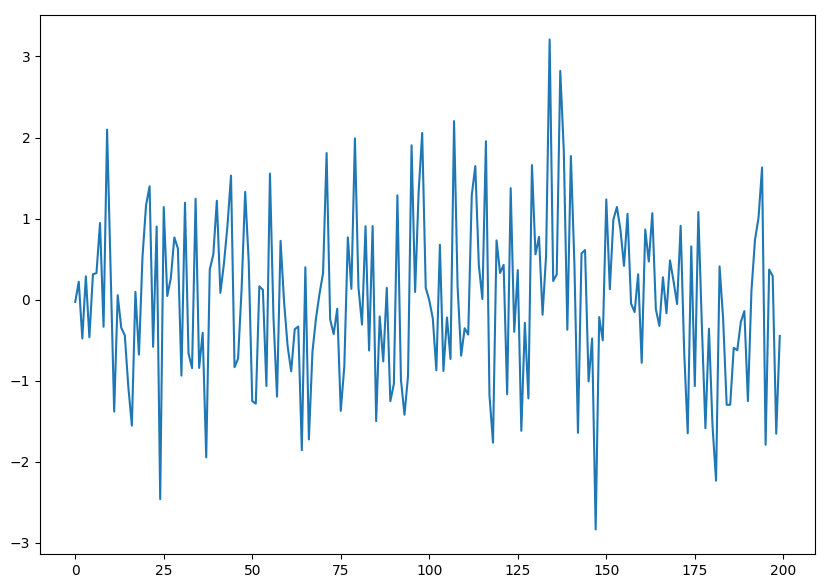
The white noise data check determines whether the input data consists of random numbers. The figure above shows an example of a regular distribution of random numbers. Random numbers cannot be analyzed meaningfully, and this data is rejected by the system. The white noise data check is performed using the classic Ljung-Box test. The test is performed over an entire time series. If you are certain that your data is not random, you can specify the wncheck=0 parameter to force TDgpt to skip this check.
TDgpt does not provide white noise checking as an independent feature. It is performed only as part of data preprocessing.
Resampling and Timestamp Alignment
Time-series data must be preprocessed before forecasting can be performed. Preprocessing is intended to resolve the following two issues:
The timestamps of real time-series datasets are not aligned. It is impossible to guarantee that devices generating data or network gateways create timestamps at strict intervals. For this reason, it cannot be guaranteed that the timestamps of time-series data are in strict alignment with the sampling rate of the data. For example, a time series sampled at 1 Hz may have the following timestamps:
['20:12:21.143', '20:12:22.187', '20:12:23.032', '20:12:24.384', '20:12:25.033']
The data returned by forecasting algorithm is strictly aligned by timestamp. For example, the next two data points in the set must be ['20:12:26.000', '20:12:27.000']. For this reason, data such as the preceding set must be aligned as follows:.
['20:12:21.000', '20:12:22.000', '20:12:23.000', '20:12:24.000', '20:12:25.000']
Resampling time-series data. The sampling rate input by the user can exceed the output rate of the results. For example, the following data was sampled at 5 second intervals, but the user could request forecasting in 10 second intervals:.
['20:12:20.000', '20:12:25.000', '20:12:30.000', '20:12:35.000', '20:12:40.000']
The data is then resampled to 10 second intervals as follows:.
['20:12:20.000', '20:12:30.000', '20:12:40.000']
This resampled data is then input into the forecasting algorithm. In this case, the data points ['20:12:25.000', '20:12:35.000'] are discarded.
It is important to note that TDgpt does not fill in missing data during preprocessing. If you input the dataset ['20:12:10.113', '20:12:21.393', '20:12:29.143', '20:12:51.330'] and specify an interval of 10 seconds, the aligned dataset will be ['20:12:10.000', '20:12:20.000', '20:12:30.000', '20:12:50.000']. This will cause the forecasting algorithm to return an error.