Dual-Replica Configuration
The features or components discussed in this document are available in TDengine TSDB-Enterprise only. TDengine TSDB-OSS does not include these features or components.
TDengine offers an arbitrator-based dual-replica solution that enables fault tolerance, provided that only one node fails at a time and failures are not continuous. Compared with three-replica deployments, dual-replica mode reduces hardware costs while ensuring a certain level of high availability.
In this architecture, leader election is handled by the high-availability mnode through arbitration, rather than being decided within the Raft group.
- Arbitrator: Provides arbitration services but does not store data. If a vgroup becomes unavailable due to a vnode failure, the arbitrator designates another vnode in the vgroup as the assigned leader, based on data synchronization status.
- Assigned Leader: A vnode that has been explicitly designated as the leader. It can continue serving client requests regardless of whether the other replica vnode is alive.
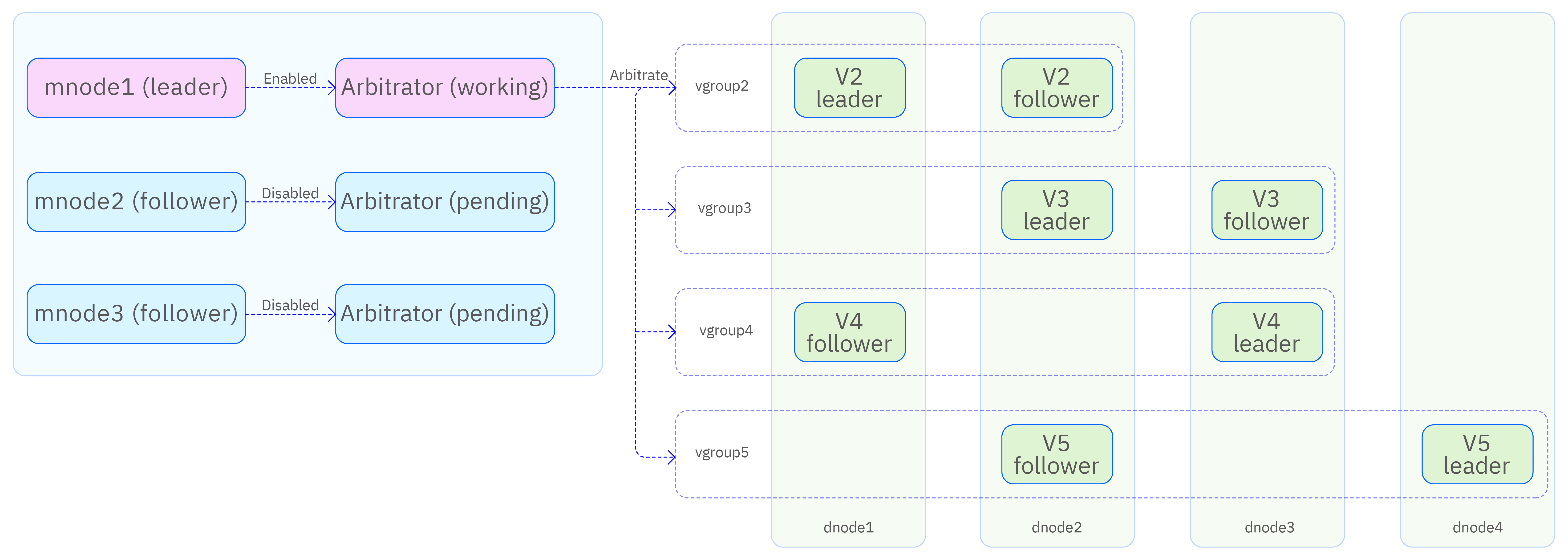
Cluster Configuration
The dual-replica architecture requires at least three server nodes. The basic deployment and configuration steps are as follows:
- Determine the number of server nodes and their hostnames or domain names, then configure DNS or /etc/hosts for proper name resolution.
- Install the TDengine TSDB-Enterprise server package on each node and edit the taos.cfg file on each node as needed.
- You can designate one node to provide only arbitration services (by deploying an mnode) and set the SupportVnodes parameter to 0, which means it does not store time-series data. This requires minimal resources (only 1–2 CPU cores) and can run alongside other applications.
- Start the taosd service on each node. Other services (such as taosadapter, taosx, taoskeeper, or taos-explorer) can be started as required.
Limitations
- The minimum server configuration is two data nodes and one arbitrator node.
- The replica count is a per-database parameter; different databases can choose the number of replicas as needed.
- The full feature set of TDengine TSDB is supported.
- All TDengine TSDB language connectors and connection methods are supported.
- You can switch between single-replica and dual-replica configurations (provided that the number of nodes, available vnodes, memory, and storage space meet the requirements).
- You cannot switch between dual-replicas and three-replica mode.
- You cannot switch from dual-replica mode to active-active mode, unless an additional independent instance is deployed to form an active-active setup.
Maintenance Commands
Create a Cluster
Create two additional dnodes in your cluster for a total of three dnodes:
CREATE dnode <dnode_ep> port <dnode_port>;
CREATE dnode <dnode_ep> port <dnode_port>;
Create mnodes on the two dnodes for a total of three mnodes:
CREATE mnode on dnode <dnode_id>;
CREATE mnode on dnode <dnode_id>;
Create a Dual-Replica Database
Create a dual-replica database:
create database <dbname> replica 2 vgroups xx buffer xx ...
Modify an Existing Database
If you have already created a single-replica database, you can change it into a dual-replica database:
alter database <dbname> replica 2;
Failure Scenarios
| Scenario | Result |
|---|---|
| Arbitrator failure (two or more mnodes down) | Service available |
| Single vnode failure after vgroup has finished synchronization | Service available |
| Double vnode failure after vgroup has finished synchronization, but one vnode recovers | You can run the ASSIGN LEADER FORCE; statement to make service available |
| Single vnode failure before vgroup has finished synchronization | Service unavailable |
| Double vnode failure | Service unavailable |
ASSIGN LEADER FORCE;
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Creating or modifying a database to use two replicas causes DB error: Out of dnodes
- Cause: There are fewer than two data nodes in the cluster.
- Solution: Ensure that there are at least two dnodes before creating a dual-replica database.
2. Creating a dual-replica database or running SPLIT VGROUP causes DB error: Vnodes exhausted
- Cause: Some dnodes have fewer available vnodes than required for database creation or vgroup splitting.
- Solution: Increase the number of CPU cores on the dnodes or modify the SupportVnodes parameter.