Apache Pulsar
The features or components discussed in this document are available in TDengine Enterprise only. TDengine OSS does not include these features or components.
This section describes how to create a data migration task through the Explorer interface to migrate data from Pulsar to the current TDengine TSDB cluster.
Feature Overview
Apache Pulsar is a cloud-native open-source distributed messaging and stream processing platform.
TDengine TSDB can efficiently read data from Pulsar and write it to TDengine TSDB to achieve historical data migration or real-time data ingestion.
Creating a Task
1. Add a Data Source
In the data writing page, click the + Add Data Source button to enter the add data source page.
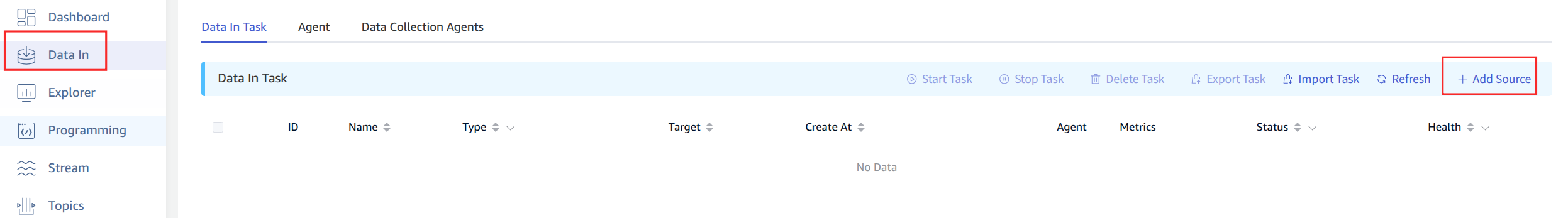
2. Configure Basic Information
Enter the task name in Name, such as: "test_pulsar";
Select Pulsar in the Type dropdown list.
Agent is optional. If needed, you can select a specific agent in the dropdown box, or click the + Create New Agent button on the right.
Select a target database in the Target Database dropdown list, or click the + Create Database button on the right.
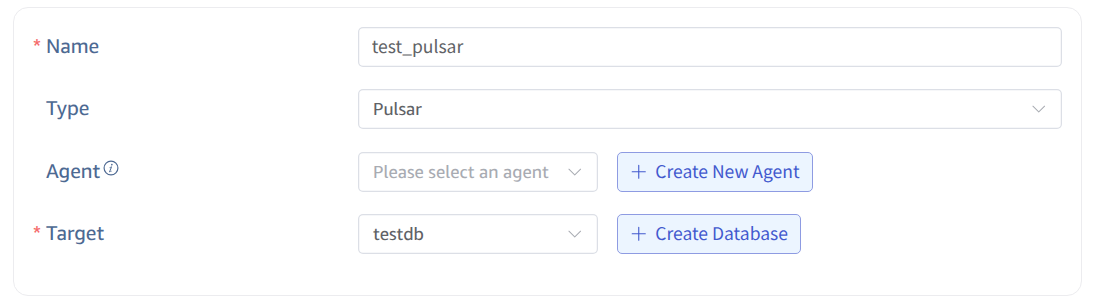
3. Configure Connection Information
Broker Server, for example: 192.168.2.131:6650.
Only one valid broker server address needs to be filled in.
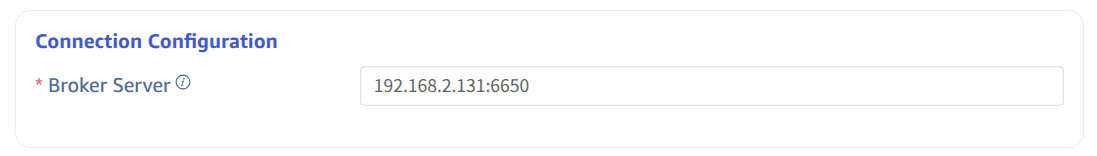
4. Authentication Mechanism
If the server has enabled authentication mechanisms, authentication information needs to be filled in here. Currently, four authentication mechanisms are supported: Basic Auth/JWT/mTLS/Custom Authentication. Please select according to the actual situation.
If authentication is not required, leave the authentication fields blank.
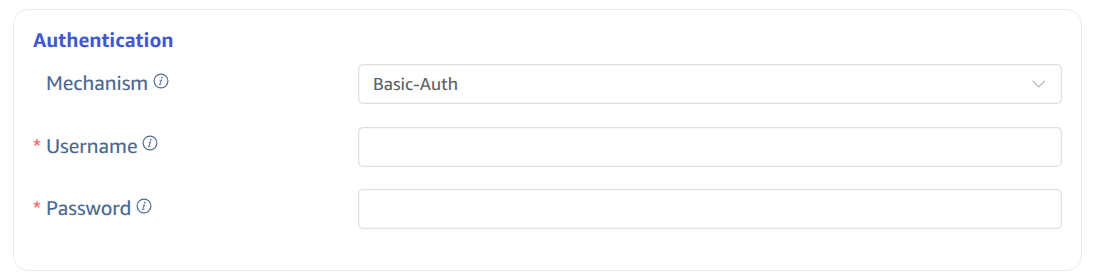
4.1. Basic Auth Authentication
Select the Basic-Auth authentication mechanism and enter the username and password:
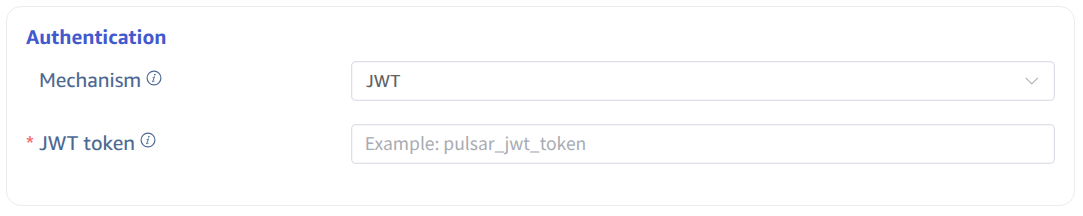
4.2. JWT Authentication
Select the JWT authentication mechanism and enter the JWT token information:
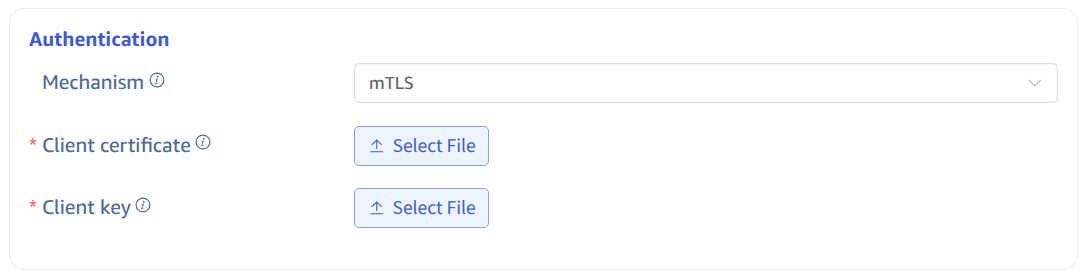
4.3. Configure mTLS Certificate Authentication
If the server has enabled mTLS encrypted authentication, you need to enable mTLS here and configure the relevant content.
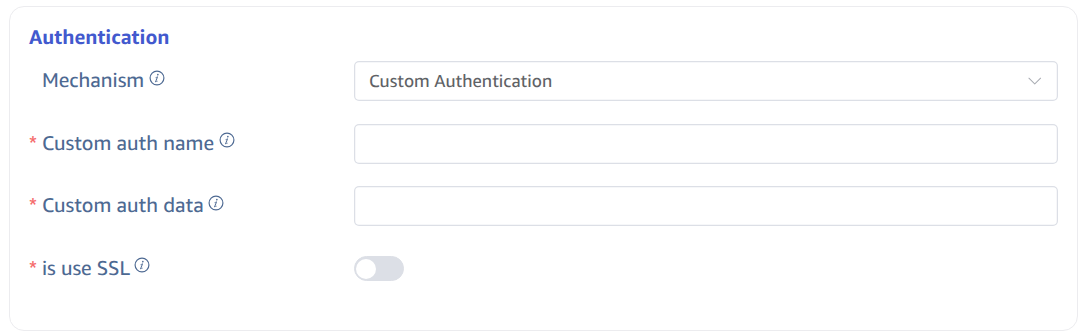
4.4. Custom Authentication
Select Custom Authentication and enter the custom authentication information provided by the server:
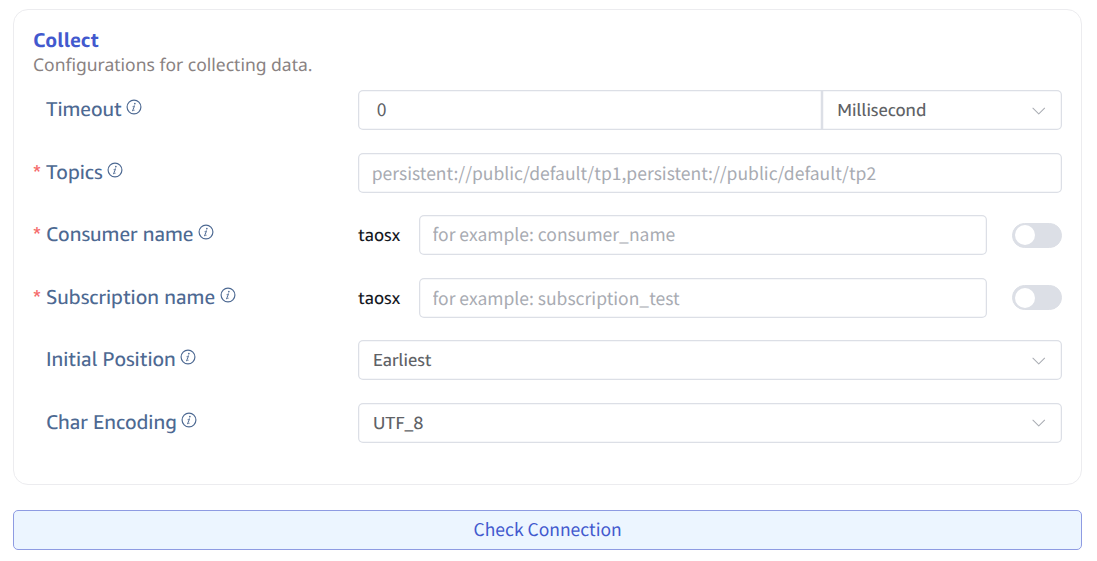
5. Configure Collection Information
Fill in the configuration parameters related to the collection task in the Collection Configuration area.
Fill in the timeout time in Timeout. When no data can be consumed from Pulsar for more than the timeout period, the data collection task will exit. The default value is 0 ms. When timeout is set to 0, it will wait indefinitely until data is available or an error occurs.
Fill in the Topic name to be consumed in Topic. Multiple Topics can be configured, separated by commas. For example: persistent://public/default/tp1,persistent://public/default/tp2.
Fill in the consumer identifier in Consumer Name. After filling, a consumer ID with the taosx prefix will be generated. If the switch at the end is turned on, the current task ID will be appended after taosx and before the input identifier.
Fill in the subscription name identifier in Subscription Name. After filling, a subscription ID with the taosx prefix will be generated. If the switch at the end is turned on, the current task ID will be appended after taosx and before the input identifier.
Select the position from which to start consuming data in the Initial Position dropdown list. There are two options: Earliest, Latest. The default value is Earliest.
- Earliest: Used to request the earliest position.
- Latest: Used to request the latest position.
In Character Encoding, configure the message body encoding format. When taosX receives a message, it uses the corresponding encoding format to decode the message body to obtain the original data. Options include UTF_8, GBK, GB18030, BIG5, with UTF_8 as the default.
Click the Connectivity Check button to check if the data source is available.
6. Configure Payload Parsing
Fill in the configuration parameters related to Payload parsing in the Payload Parsing area.
6.1 Parsing
There are three methods to obtain sample data:
Click the Retrieve from Server button to get sample data from Pulsar.
Click the File Upload button to upload a CSV file and obtain sample data.
Enter sample data from the Pulsar message body in Message Body.
JSON data supports JSONObject or JSONArray, and the following data can be parsed using a JSON parser:
{"id": 1, "message": "hello-world"}
{"id": 2, "message": "hello-world"}
or
[{"id": 1, "message": "hello-world"},{"id": 2, "message": "hello-world"}]
The parsing results are shown as follows:
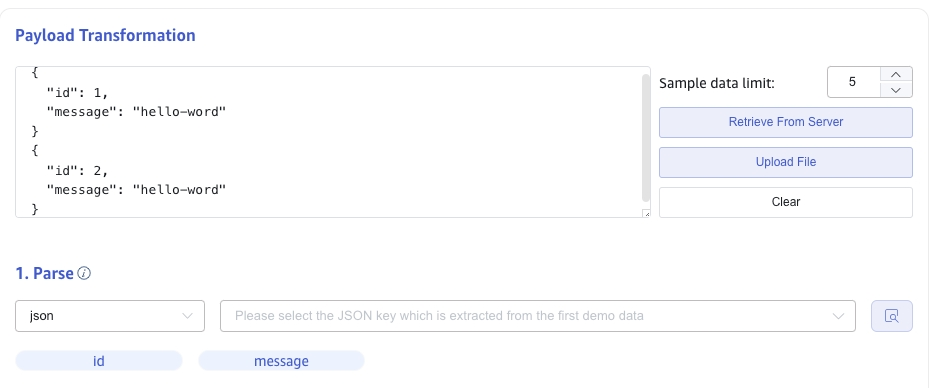
Click the magnifying glass icon to view the preview parsing results.
6.2 Field Splitting
In Extract or Split from Columns, fill in the fields to extract or split from the message body, for example: split the message field into message_0 and message_1, select the split extractor, fill in the separator as -, and number as 2.
Click Add to add more extraction rules.
Click Delete to delete the current extraction rule.
Click the magnifying glass icon to view the preview extraction/splitting results.
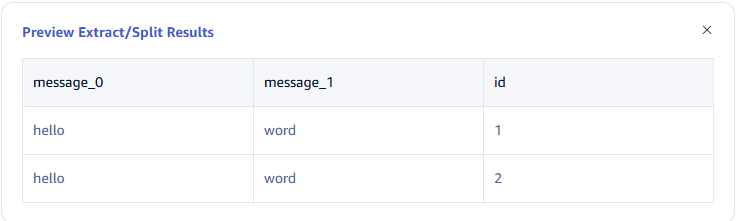
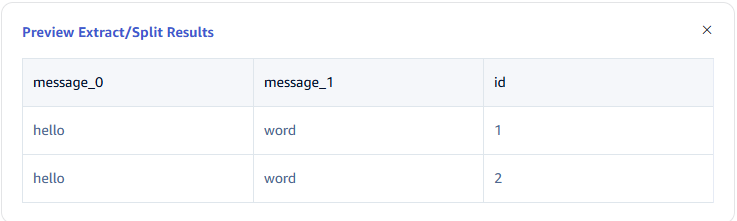
6.3 Data Filtering
In Filter, fill in the filtering conditions, for example: enter id != 1, then only data with id not equal to 1 will be written to TDengine.
Click Add to add more filtering rules.
Click Delete to delete the current filtering rule.
Click the magnifying glass icon to view the preview filtering results.
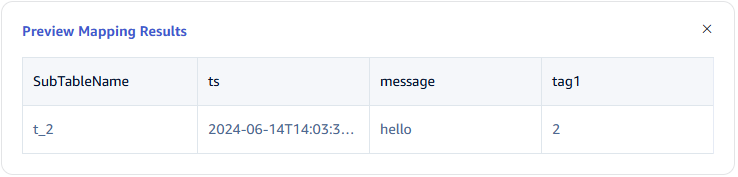
6.4 Table Mapping
In the Target Supertable dropdown, select a target supertable, or click the Create Supertable button on the right.
In the Mapping section, fill in the name of the subtable in the target supertable, for example: t_{id}. Fill in the mapping rules as required, where mapping supports setting default values.

Click Preview to view the results of the mapping.
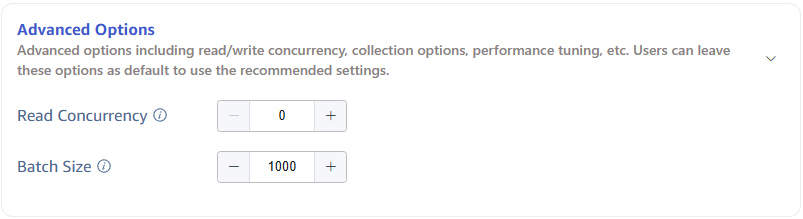
7. Configure Advanced Options
The Advanced Options area is collapsed by default, click the > on the right to expand it, as shown below:
8. Completion of Creation
Click the Submit button to complete the creation of the Pulsar to TDengine data synchronization task. Return to the Data Source List page to view the status of the task execution.